Last week, Google made a significant announcement by introducing Ironwood, its seventh generation Tensor Processing Unit (TPU). Unveiled at the Google Cloud Next 25 event, this new chip is said to be the company's most powerful and scalable custom artificial intelligence (AI) accelerator to date. Specifically designed for AI inference, Ironwood aims to provide high performance and efficiency.
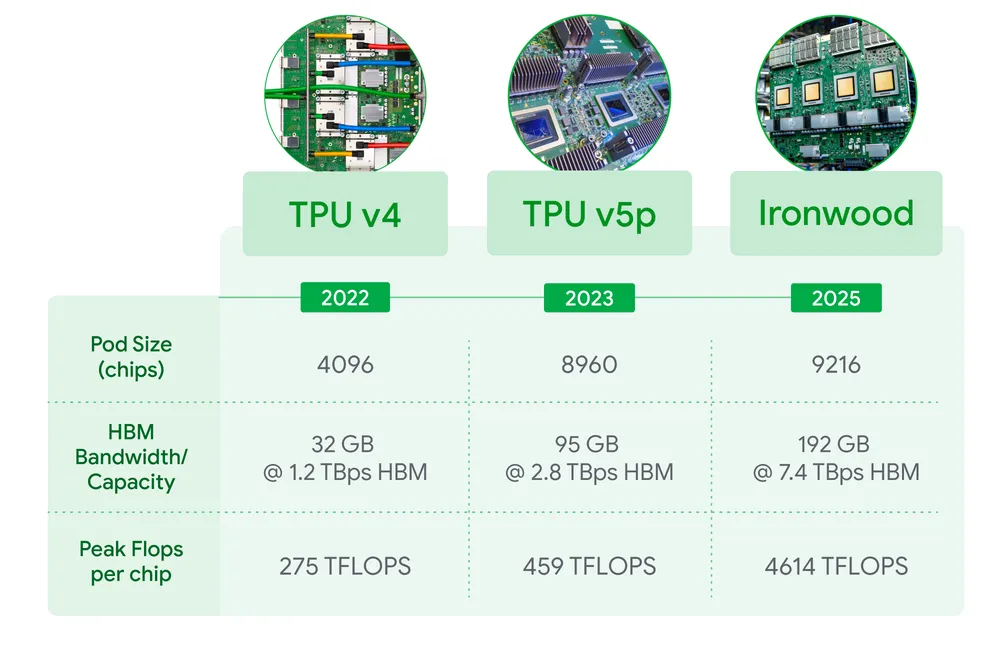
Google highlighted that Ironwood will be available in two sizes, based on AI workload demands: a 256 chip configuration and a larger 9,216 chip design. Boasting over 42.5 exaflops of compute power, Ironwood surpasses the performance of the world's fastest supercomputer by a staggering 24 times. Leading AI models, such as Gemini 2.5 and the Nobel Prize-winning AlphaFold, are anticipated to leverage Ironwood's capabilities. Amin Vahdat, Vice President at Google Cloud, noted that Ironwood is tailored to gracefully handle the complex computational and communication requirements of "thinking models."
One of Ironwood's standout features is its significant memory capacity, with each chip housing 192 GB of high-bandwidth RAM and achieving nearly 7.4 TB/s of memory throughput. This represents a sixfold improvement over the previous generation Trillium TPU. Additionally, Ironwood incorporates the advanced SparseCore technology, designed to enhance performance across various AI tasks.
Google plans to launch Ironwood to its Cloud customers by late this year. This innovation holds considerable significance in boosting Google’s competitive edge against other tech giants in the AI accelerator space. Companies like Amazon and Microsoft are also developing their AI chips, and with Ironwood, Google aims to more efficiently manage the rising demands of AI workloads, potentially reshaping corporate strategies surrounding AI implementations.