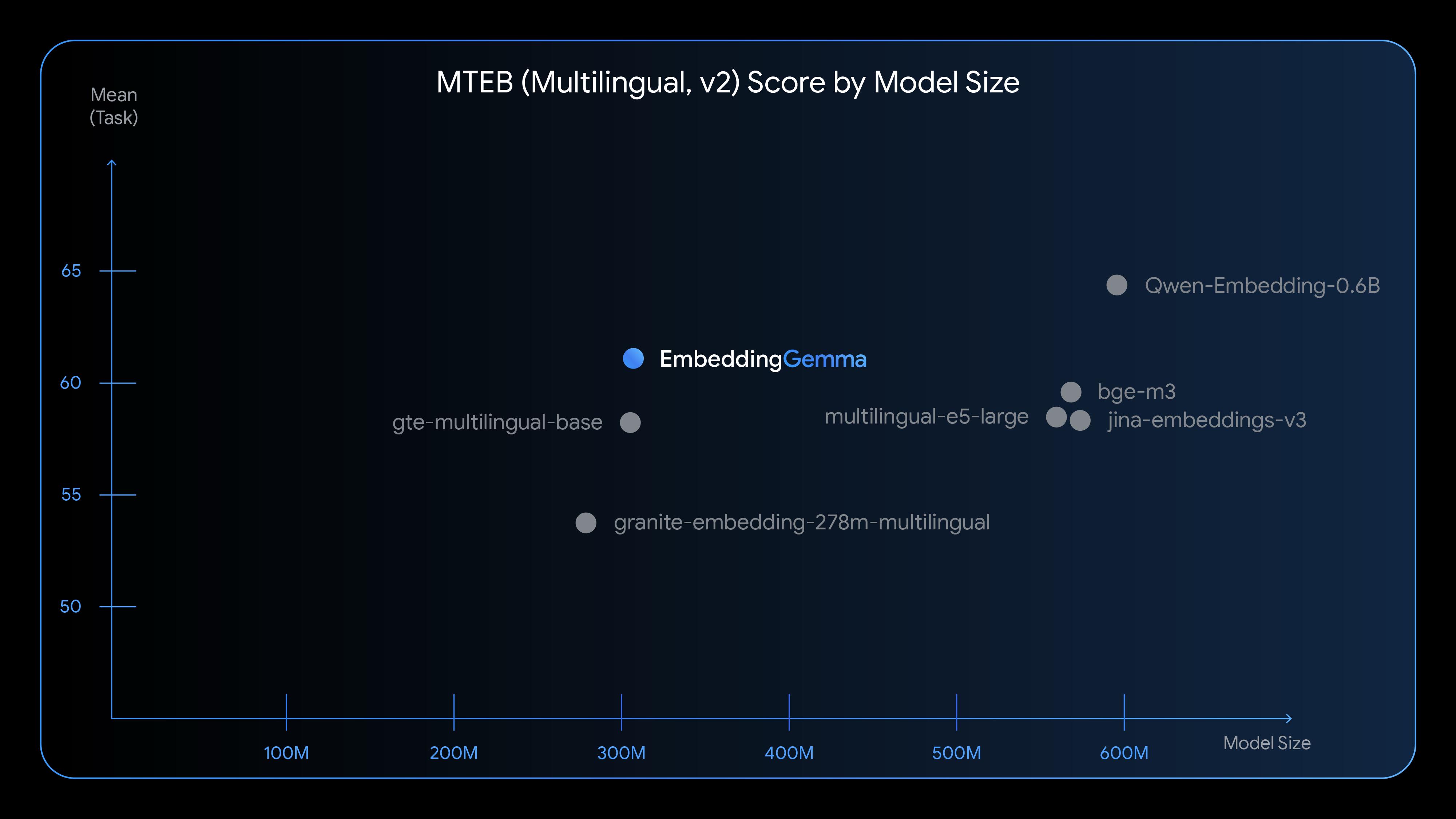
Tech giant Google has introduced EmbeddingGemma, a groundbreaking model poised to revolutionize the AI landscape. This state-of-the-art multilingual embedding model is specifically engineered for high speed and efficiency, particularly for on-device and everyday use cases. Boasting 308 million parameters and built on the Gemma 3 architecture, EmbeddingGemma ranks among the top open-source models in its size class on the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB). This model introduces novel techniques designed to increase efficiency and improve performance in mobile-first AI applications.
EmbeddingGemma utilizes new approaches, including what Google calls "elastic inference," which allows developers to choose either the full model or its faster, yet fully functional, sub-model. In the future, it will offer full support for elastic inference, enabling dynamic switching between the full model and the sub-model on the fly, depending on the current task and device load. Additionally, a new feature designed to accelerate inference, known as "KV cache sharing," significantly reduces the time-to-first-token, a critical metric for applications delivering streaming responses.
This advanced model is optimized to run on everyday devices like mobile phones, laptops, and desktops, offering customizable output dimensions ranging from 768 down to 128 (thanks to Matryoshka representation learning) and a 2K token context window. EmbeddingGemma, especially when used in conjunction with Gemma 3n for enhanced mobile AI inference, unlocks new use cases for mobile RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) pipelines, semantic search, and more.
To ensure easy accessibility for developers, Google has prioritized integrations with popular tools such as sentence-transformers, llama.cpp, MLX, Ollama, and LMStudio. This widespread support allows developers to quickly integrate this powerful model into their projects, enabling the development of privacy-centric, flexible on-device AI applications. Google is also paving the way for new capabilities, such as performing offline searches across personal files, texts, emails, and notifications, ensuring sensitive user data remains secure.